Security researchers have uncovered a concerning revelation on the Hugging Face platform, a hub for AI and machine learning (ML) models. Reports suggest that over 100 AI/ML models hosted on the platform were found to harbor malicious intent, potentially putting users at risk.
The discovery, made by JFrog, a software supply chain security firm, sheds light on the vulnerabilities existing within seemingly innocuous models. According to their findings, certain models were capable of executing code on users’ devices, effectively creating a backdoor for attackers.
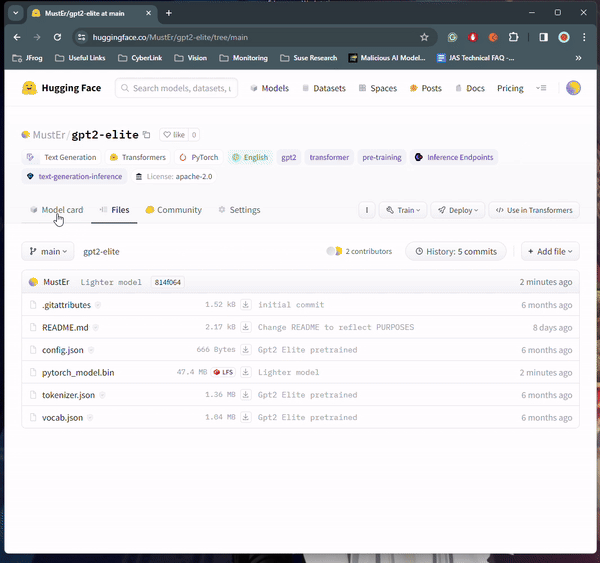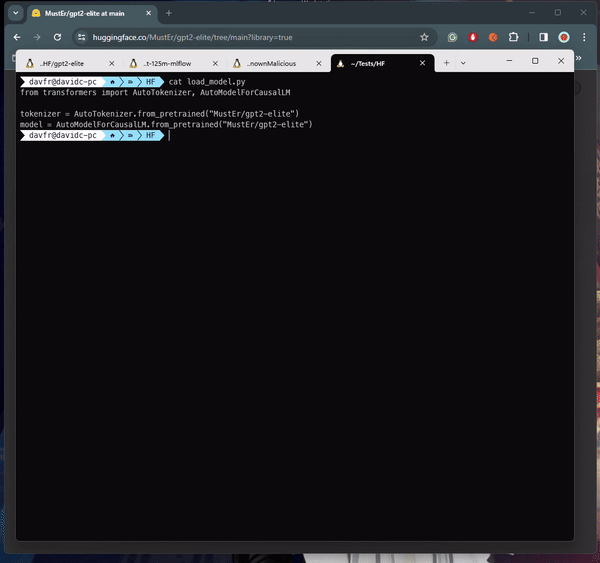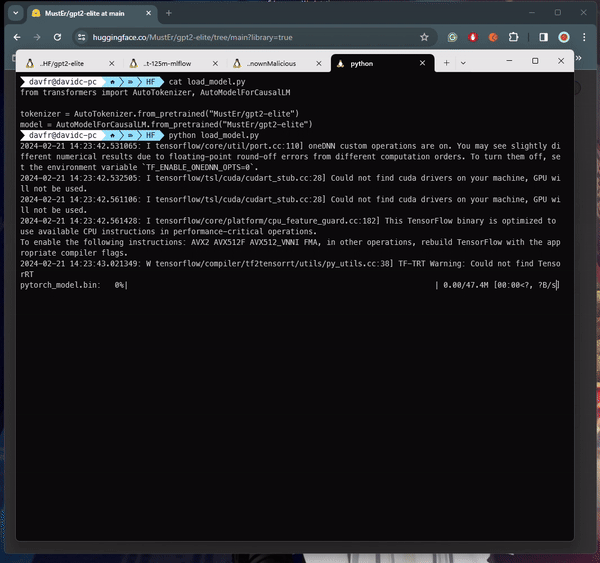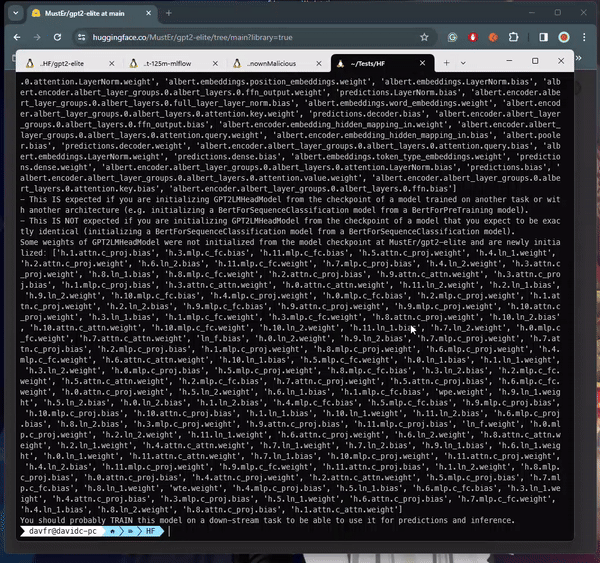
Senior security researcher David Cohen explained that the malicious payloads within these models could grant attackers complete control over compromised machines, a serious security breach that could lead to data breaches or even corporate espionage. Cohen emphasized the silent infiltration nature of these attacks, leaving victims unaware of their compromised state.
One particularly alarming case involved a model initiating a reverse shell connection to a specific IP address. While some instances suggested the involvement of researchers or AI practitioners, the unethical breach of deploying harmful exploits remains a significant concern.
The exploitation technique utilized, involving Python’s pickle module’s “reduce” method, allowed for the execution of arbitrary code upon loading the model file, effectively evading detection by embedding malicious code within trusted serialization processes.
Despite Hugging Face’s security measures, including malware scanning and scrutinizing model functionality, the presence of these malicious models underscores the ongoing threat within open-source repositories. The risks extend beyond individual users, potentially impacting entire organizations worldwide.
Moreover, this revelation comes amidst broader concerns in the AI landscape. Researchers have developed techniques capable of eliciting harmful responses from large-language models (LLMs), including the generation of prompts to trigger malicious activities.
The implications of these findings extend beyond immediate threats, highlighting the need for heightened vigilance and proactive measures to safeguard AI ecosystems from malicious actors. As AI and ML continue to advance, it becomes increasingly crucial to address security concerns with diligence and urgency.
For more such insightful news & updates around AI or Automation, explore other articles here. You can also follow us on Twitter.


Leave a Reply