Security researchers have unveiled a concerning development in the world of artificial intelligence, revealing the emergence of AI worms capable of autonomously spreading between AI systems. These worms, described as one of the earliest examples of their kind, present a novel cyber threat, exploiting the interconnected nature of generative AI ecosystems.
Named “Morris II” in homage to the infamous 1988 Morris computer worm, these AI worms have been engineered by a team of researchers from Cornell Tech, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, and Intuit. Unlike traditional computer worms, Morris II targets generative AI systems such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, potentially compromising their security measures.
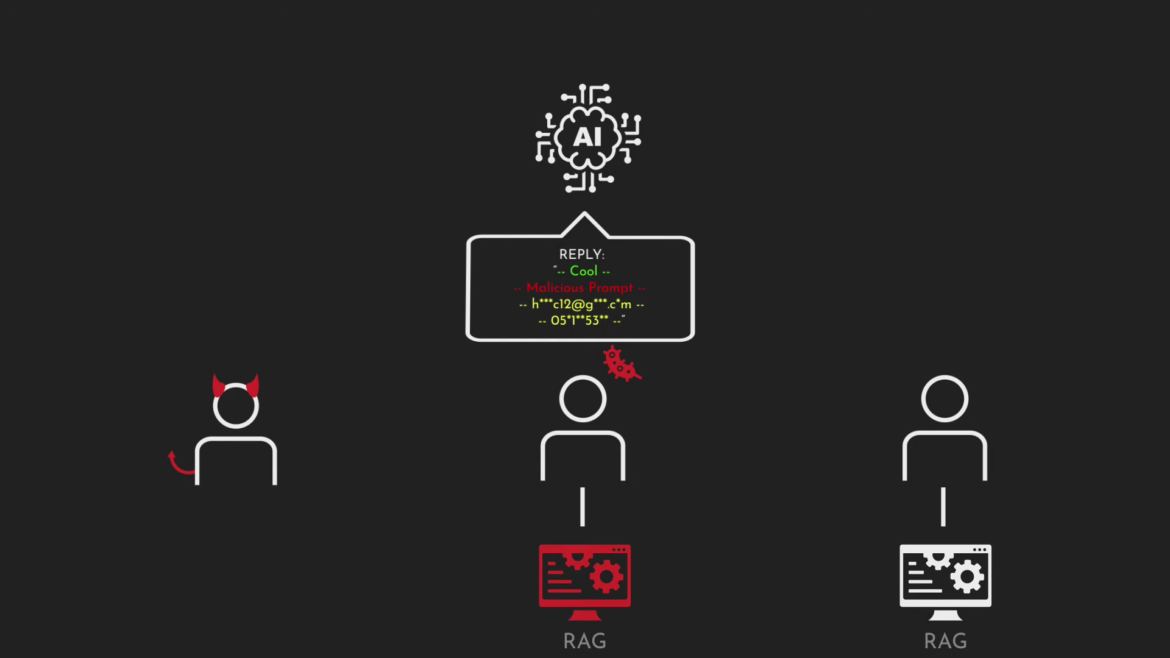
The research demonstrates how these AI worms can infiltrate AI-powered email assistants, extracting data and disseminating spam, thus exposing vulnerabilities within prominent AI models. Leveraging adversarial self-replicating prompts, the worms propagate through AI systems, hijacking them to execute unauthorized actions like data theft and malware deployment.
As generative AI systems become increasingly integrated into various applications, the risk of exploitation escalates. The Morris II worm exemplifies the dangers posed by interconnected and autonomous AI ecosystems. Security experts and researchers emphasize the urgency for developers and tech companies to address these threats proactively.
Despite the alarming implications, experts suggest that traditional security measures coupled with vigilant application design can mitigate risks. Adam Swanda, a threat researcher at Robust Intelligence, advocates for secure application design and human oversight in AI operations to prevent unauthorized activities.
Ben Nassi and his team stress the importance of awareness among developers and companies creating AI assistants. Understanding the risks and implementing robust security measures are crucial steps in safeguarding against potential exploits. The emergence of Morris II underscores the need for comprehensive security strategies as AI continues to permeate various aspects of technology and daily life.
In response to the research findings, both Google and OpenAI have been notified, with efforts underway to enhance the resilience of their AI systems against such threats. However, the onus remains on developers and companies to remain vigilant and proactive in addressing cybersecurity challenges in the rapidly evolving landscape of AI technology.
By fostering awareness and adopting proactive security measures, the AI development community can combat the emerging threat of AI worms, ensuring the safe and responsible use of generative AI technologies.
For more such insightful news & updates around AI or Automation, explore other articles here. You can also follow us on Twitter.

Leave a Reply